-
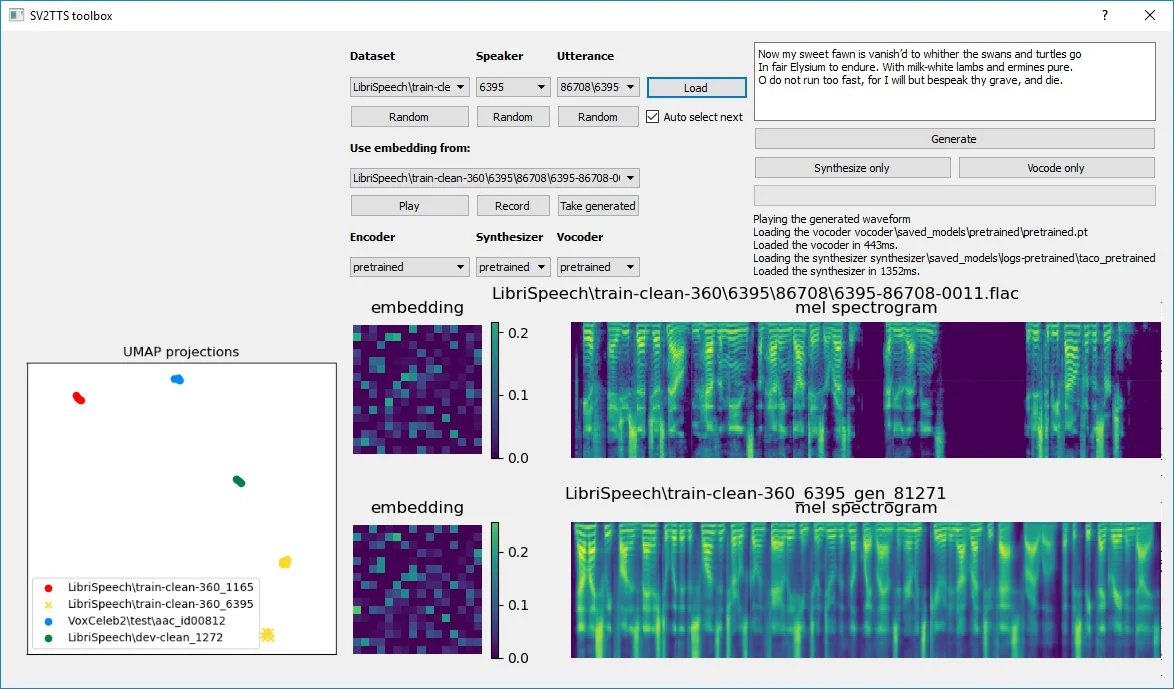
My laboratories
-
-
 Clothes Try-On
Convolutional Networks
Clothes Try-On
Convolutional Networks
-
 CNN GANS
BRAND & PRODUCT 3D RENDER
Text to Video.
CNN GANS
BRAND & PRODUCT 3D RENDER
Text to Video.
-
-
-
 LLM'S NPL-TRY
Fine-tunning Transformers
LLM'S NPL-TRY
Fine-tunning Transformers
-
 Elastic Net Lasso
INFERENCE LLMS
Elastic Net Lasso
INFERENCE LLMS
-
-
-
 LSTM
difussion transformers
LSTM
difussion transformers
-
 Caption music tracks
Text to music.
Caption music tracks
Text to music.
-
- About Me
- Services
- GenAI Video
- Blog
- Finance